线性结构和非线性结构
线性结构
1) 线性结构作为最常用的数据结构,其特点是数据元素之间存在一对一的线性关系
2) 线性结构有两种不同的存储结构,即顺序存储结构(数组)和链式存储结构(链表)。顺序存储的线性表称为顺序表,顺序表中的存储元素是连续的
3) 链式存储的线性表称为链表,链表中的存储元素不一定是连续的,元素节点中存放数据元素以及相邻元素的地址信息
4) 线性结构常见的有:数组,队列,链表和栈
非线性结构
非线性结构包括:二维数组,多维数组,广义表,树结构,图结构
稀疏数组和队列
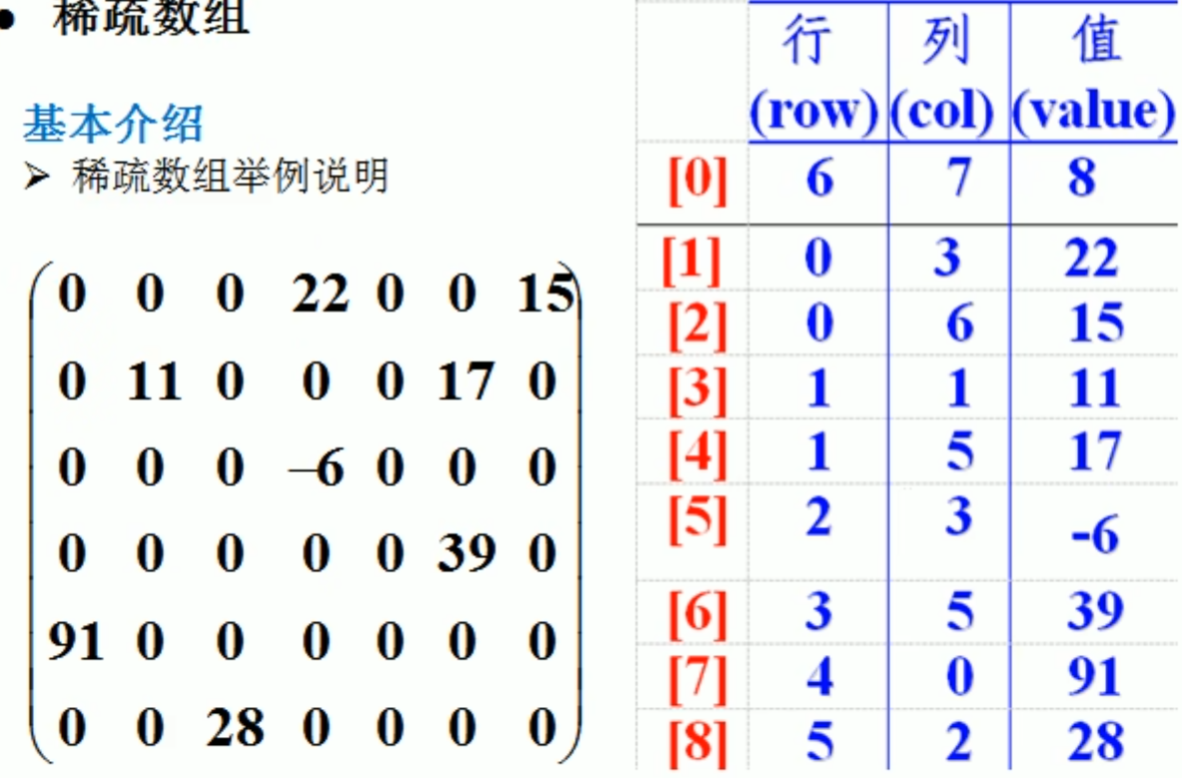
稀疏数组
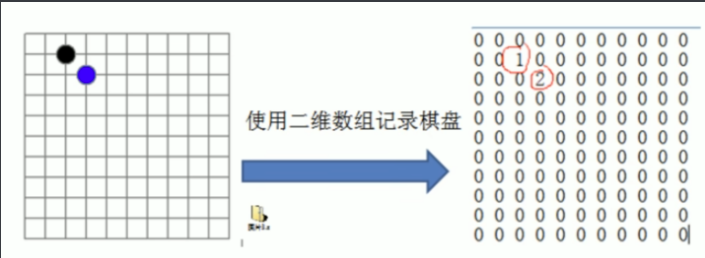
分析问题:
因为该二维数组的很多值是默认值0.因此记录了很多没有意义的数据->稀疏数组
基本介绍
当一个数组大部分是0,或者为同一个值的数组时,可以使用稀疏数组来保存该数组。
稀疏数组的处理方法是:
1) 记录数组一共有几行几列,有多少个不同的值
2) 把具有不同值的元素的行列及值记录在一个小规模的数组中,从而缩小程序的规模
稀疏数组案例
左边的为原始的二维数组经过处理后变成右边的稀疏数组
应用实例
1.使用稀疏数组,来保留类似前面的二维数组(棋盘,地图)
2.把稀疏数组存盘,并且可以从新恢复原来的二维数数组
3.整体思路分析
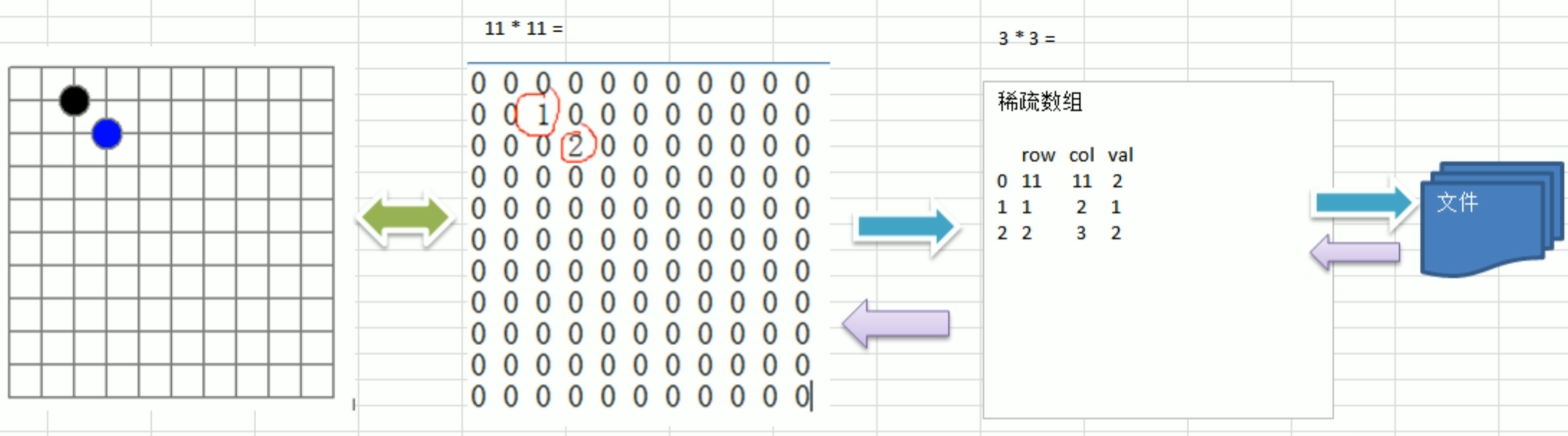
二维数组转稀疏数组的思路(“()”为[])
1.遍历 原始的二维数组,得到有效数据的个数sum
2.根据sum就可以创建稀疏数组sparseArr int(sum +1)(3)
3.将二维数组的有效数据数据存入到稀疏数组
稀疏数组转原始的二维数组的思路
1.先读取稀疏数组的第一行,根据第一行的数据,创建原始的二维数组,比如上面的chessArr2 = int (11)(11)
2.在读取稀疏数组后几行的数据,并赋给原始的二维数组即可
4.代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
| public class spareArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int chessArr1[][] = new int[11][11];
chessArr1[1][2] = 1;
chessArr1[2][3] = 2;
System.out.println("原始的二维数组");
for (int[] row : chessArr1) {
for(int data:row){
System.out.printf("%d\t",data);
}
System.out.println();
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chessArr1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chessArr1.length; j++) {
if (chessArr1[i][j] != 0){
sum++;
}
}
}
int sparseArr[][] = new int[sum+1][3];
sparseArr[0][0] = 11;
sparseArr[0][1] = 11;
sparseArr[0][2] = sum;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chessArr1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chessArr1.length; j++) {
if (chessArr1[i][j] != 0){
count++;
sparseArr[count][0]=i;
sparseArr[count][1]=j;
sparseArr[count][2]=chessArr1[i][j];
}
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("得到的稀疏数组为:");
for (int i = 0; i < sparseArr.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d\t%d\t%d\t\n",sparseArr[i][0],sparseArr[i][1],sparseArr[i][2]);
}
System.out.println();
int chessArr2[][] = new int[sparseArr[0][0]][sparseArr[0][1]];
for (int i = 1; i < sparseArr.length; i++) {
chessArr2[sparseArr[i][0]][sparseArr[i][1]]=sparseArr[i][2];
}
System.out.println("稀疏数组还原成原始数组");
for (int[] row : chessArr1) {
for(int data:row){
System.out.printf("%d\t",data);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
|
队列
队列介绍
队列是一个有序列表,可以用数组或是链表来实现
遵循先入后出的原则。即:先存入队列的数据,要先取出。后存入的要后取出
数组模拟队列
队列本身是有序列表,若使用数组的结构来存储队列的数据,则队列数组的声明如下图,其中maxSize是该队列的最大容量。
因为队列的输出,输入是分别从前后端来处理,因此需要两个变量front及rear分别记录队列前后端的下标,front会随着数据输出而改变,而rear则是随着数据输入而改变
当我们将数据存入队列时称为”addQueue”,addQueue的处理需要有两个步骤:
1.将尾指针往后移:rear+1,当front == rear[空]
2.若尾指针rear小于队列的最大下标maxSize-1,则将数据存入rear所指的数组元素中,否则无法存入数据。rear == maxSize -1 [队列满]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| package 数据结构.队列;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
arryqueue arryqueue = new arryqueue(3);
int key = ' ';
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
while (loop){
System.out.println("1.显示队列");
System.out.println("2.添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("3.从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("4.查看队列头数据");
System.out.println("5.退出程序");
key = sc.nextInt();
switch (key){
case 1:
arryqueue.list();
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("输入一个数字");
int value = sc.nextInt();
arryqueue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 3:
try {
int res = arryqueue.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n",res);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 4:
try {
int res = arryqueue.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列头的数据是%d\n",res);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 5:
sc.close();
loop=false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| package 数据结构.队列;
public class arrque {
}
class arryqueue{
private int maxsize;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int[] arr;
public arryqueue(int maxsizearr){
maxsize = maxsizearr;
arr = new int[maxsize];
front = 0;
rear = 0;
}
public boolean isfull(){
return rear == maxsize -1;
}
public boolean isempty(){
return rear == front;
}
public void addQueue(int n){
if (isfull()){
System.out.printf("队列满,不能加入");
return;
}
rear++;
arr[rear] = n;
}
public int getQueue(){
if (isempty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据");
}
front++;
return arr[front];
}
public void list(){
if (isempty()){
System.out.println("队列空");
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n",i,arr[i]);
}
}
public int headQueue(){
if (isempty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列空没有数据");
}
return arr[front+1];
}
}
|
问题:
1.目前数组使用一次就不能用,没有达到复用的效果
2.将这个数组使用算法,该进程一个环形的队形 取模: %
数组模拟环形队列
思路如下:
1.front变量的含义做一个调整:front就指向队列的第一个元素,也就是说arr[front]就是队列的第一个元素,front的初始值=0
2.rear变量的含义做一个调制:rear指向队列的最后一个元素的后一个位置,因为i希望空出一个空间做为约定,rear的初始值=0
3.当队列满时,条件是(rear + 1)%maxSize = front[满]
4.队列为空的条件,rear == front[空]
5.队列中有效的数据的个数(rear + maxSize - front)%maxSize
修改后代码演示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| package 数据结构.队列;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class circlequeue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
circlearray circlearray = new circlearray(5);
int key = ' ';
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
while (loop){
System.out.println("1.显示队列");
System.out.println("2.添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("3.从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("4.查看队列头数据");
System.out.println("5.退出程序");
key = sc.nextInt();
switch (key){
case 1:
circlearray.list();
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("输入一个数字");
int value = sc.nextInt();
circlearray.addQueue(value);
break;
case 3:
try {
int res = circlearray.getQueue();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是%d\n",res);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 4:
try {
int res = circlearray.headQueue();
System.out.printf("队列头的数据是%d\n",res);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 5:
sc.close();
loop=false;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
| package 数据结构.队列;
public class circlearrqueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
class circlearray{
private int maxsize;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int[] arr;
public circlearray(int maxsizearr){
maxsize = maxsizearr;
arr = new int[maxsize];
front = 0;
rear = 0;
}
public boolean isfull(){
return ((rear + 1) % maxsize == front);
}
public boolean isempty(){
return rear == front;
}
public void addQueue(int n){
if (isfull()){
System.out.printf("队列满,不能加入");
return;
}
arr[rear] = n;
rear = (rear + 1) % maxsize;
}
public int getQueue(){
if (isempty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列空,不能取数据");
}
int value = arr[front];
front = (front+1)%maxsize;
return value;
}
public void list(){
if (isempty()){
System.out.println("队列空");
return;
}
for (int i = front; i < front+size(); i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i % maxsize ,arr[i % maxsize]);
}
}
public int size(){
return (rear + maxsize - front)%maxsize;
}
public int headQueue(){
if (isempty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列空没有数据");
}
return arr[front];
}
}
|
链表
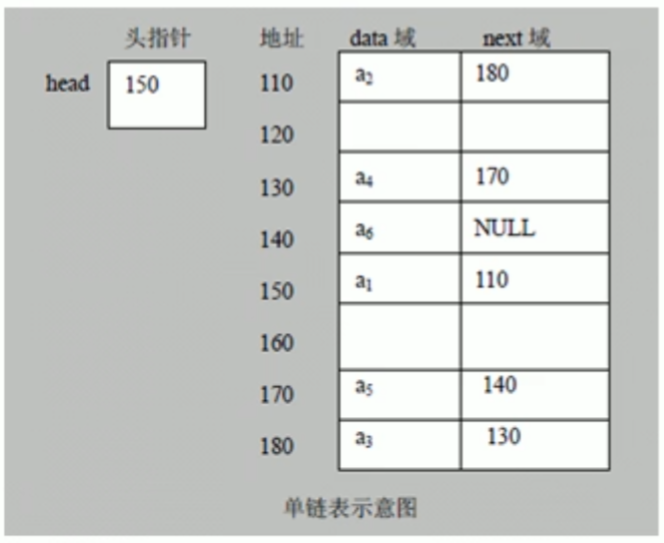
链表是有序的列表,但是它在内存中是存储如下
1.链表是以节点的方式来存储,是链式存储
2.每个节点包含data域用于存储数据,next域:指向下一个节点
3.如图:链表的各个节点不一定是连续存储
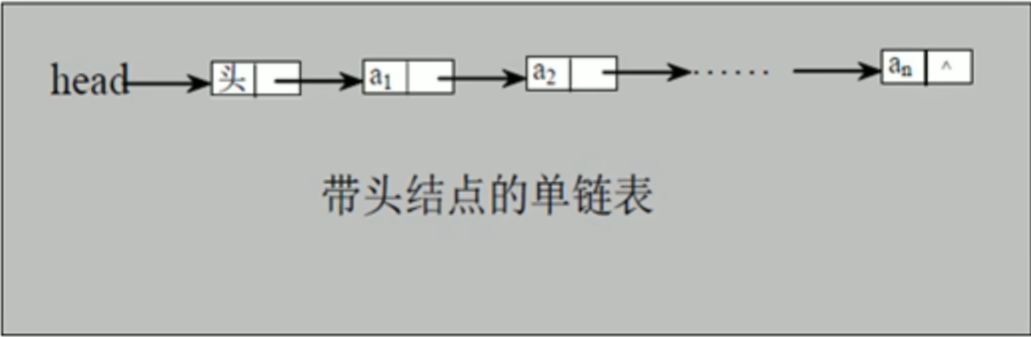
4.链表分带头节点的链表和没有头节点的链表,根据实际的需求来确定
单链表
单链表(带头结点)逻辑结构示意图如下
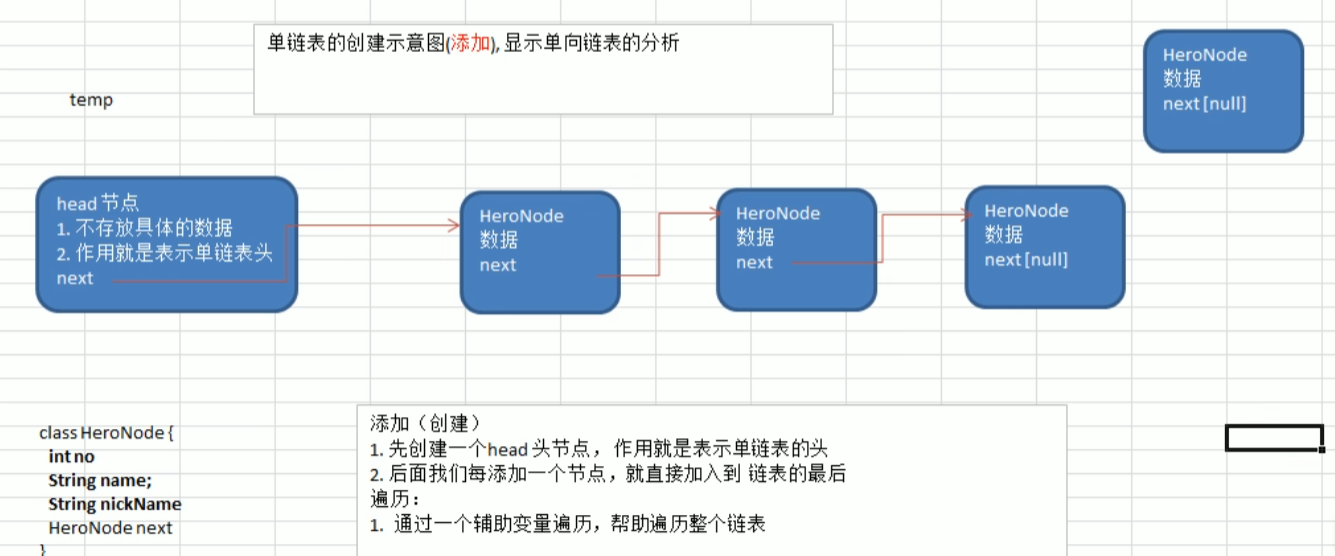
单链表应用实例
按照顺序添加
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| package 数据结构.链表;
public class Linkedlist {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeroNode hero1 = new HeroNode(1,"1","01");
HeroNode hero2 = new HeroNode(2,"2","02");
HeroNode hero3 = new HeroNode(3,"3","03");
HeroNode hero4 = new HeroNode(4,"4","04");
SingleLinkedList singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList();
singleLinkedList.add(hero1);
singleLinkedList.add(hero3);
singleLinkedList.add(hero2);
singleLinkedList.add(hero4);
singleLinkedList.list();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| package 数据结构.链表;
public class LKlist {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
class SingleLinkedList{
private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0,"","");
public void add(HeroNode heroNode){
HeroNode temp= head;
while (true){
if (temp.next == null){
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = heroNode;
}
public void list(){
if (head.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next;
while (true){
if (temp == null){
break;
}
System.out.println(temp);
temp=temp.next;
}
}
}
class HeroNode{
public int no;
public String name;
public String nickname;
public HeroNode next;
public HeroNode(int no,String name,String nickname){
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "HeroNode[no="+no+",name="+name+",nickname="+nickname+"]";
}
}
|
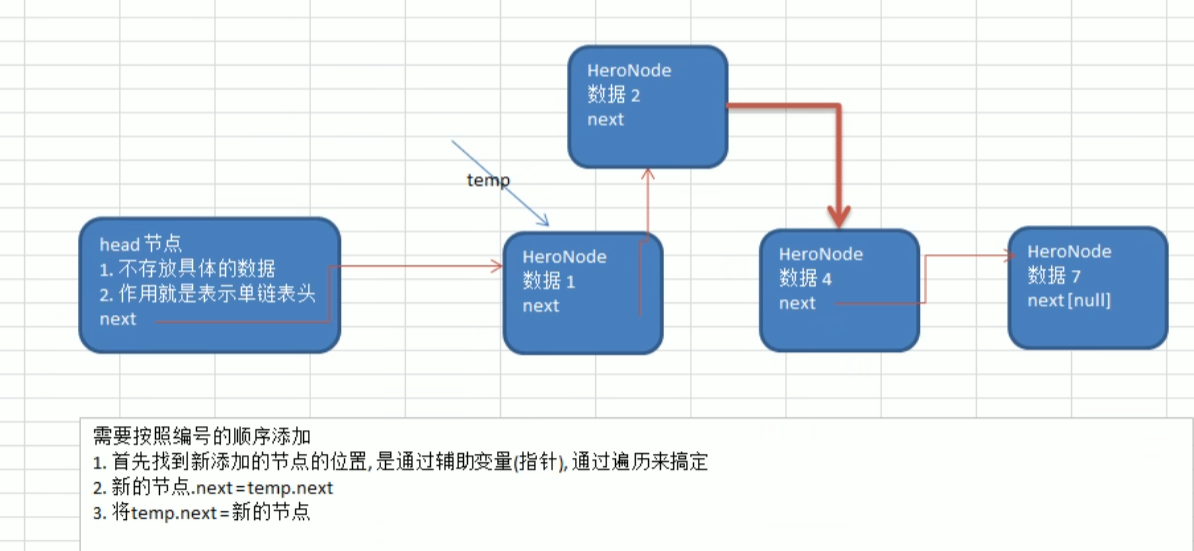
自动排序添加和修改编号代码
代码思路图
1.找到节点,通过遍历
2.temp.name = newHeroNode.name;
temp.nickname=newHeroNode.nickname;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public void addBy(HeroNode heroNode){
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;
while (true){
if (temp.next == null){
break;
}
if (temp.next.no > heroNode.no){
break;
} else if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {
flag =true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag){
System.out.printf("准备输入的数据的编号%d已存在,不能插入\n",heroNode.no);
}else {
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public void update(HeroNode newHeroNode){
if (head.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;
while (true){
if (temp == null){
break;
}
if (temp.no == newHeroNode.no){
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag){
temp.name = newHeroNode.name;
temp.nickname = newHeroNode.nickname;
}else {
System.out.printf("没有找到编号%d的节点,不能修改\n",newHeroNode.no);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
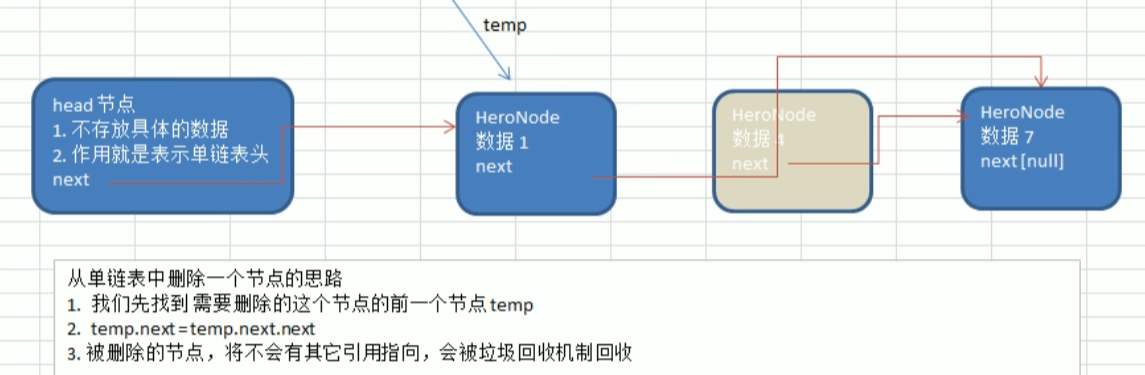
public void del(int no){
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;
while (true){
if (temp.next == null){
break;
}
if (temp.next.no == no){
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}else {
System.out.printf("要删除的%d节点不存在\n",no);
}
}
|